- What Is an Adverb?
- Learning about Adverbs:
- Identification of Adverbs:
- (First Point) Adverbs modify verbs, but they can also modify adjectives and other adverbs.
- (Second Point) While many adverbs end in "-ly," there are many that do not.
- (Third Point) In actual sentences, many adverbs are phrases or clauses rather than single words.
- Adverbs Modify Verbs
An adverb is also a part of speech that supplements a verb, an adjective, another adverb or even … a sentence. It gives further details about when, where, how, or to what extent something occurs, or is carried out. Adverbs are used to answer questions as to how?, when., where?. And to what extent?.
What Is an Adverb?
An adverb is a word which indicates some action or condition associated with the verb, with an adjective, another adverb, or with the whole sentence. Adverbs giv details as to how, when, where, to what degree or in what way something happens.
- She quickly finished her homework.
Learning about Adverbs:
When first introduced to adverbs, we tend to focus on adverbs that describe and therefore qualify verbs. In the following examples, the adverbs indicate how the verbs are performed:
- He runs fast.
Identification of Adverbs:
(First Point) Adverbs modify verbs, but they can also modify adjectives and other adverbs.
- She is incredibly talented.
(Second Point) While many adverbs end in "-ly," there are many that do not.
- fast, never, well, very, most, least, more, less, now, far, there.
(Third Point) In actual sentences, many adverbs are phrases or clauses rather than single words.
Adverbs Modify Verbs
Adverbs can tell how, when, where, or to what extent anything or anybody is done and are always related to verbs. Here’s a brief overview:
Key Points:
How: They can also show how an action was done, is being done or is going to be done.
When: Information gathered from them can inform a decision at what time a certain action should be taken.
Where: Adverbs can indicate where the action takes place..
To What Extent: They can indicate the amount, or extent of the action.
Here are some examples of adverbs modifying verbs:
- He quickly finished his homework.
- She will call you later.
- They ran outside.
- He almost forgot her birthday.
Adverbs Modify Adjectives
Adverbs can also modify adjectives, providing more detail about the quality, degree, or intensity of the adjective they modify. This allows for more precise descriptions.
Key Points:
- Enhancement: Adverbs can amplify or diminish the quality described by the adjective.
- Position: Typically, adverbs modifying adjectives are placed before the adjective.
Here are some examples of adverbs modifying adjectives:
- She is incredibly talented.
The movie was extremely boring.
He is quite tall.
Adverbs Modify Adverbs
Adverbs can also modify other adverbs, providing additional information about the intensity, degree, or manner of the action described. This helps to create a more nuanced understanding of the action.
Here are some examples of adverbs modifying adverbs:
- She ran very quickly.
He speaks quite softly.
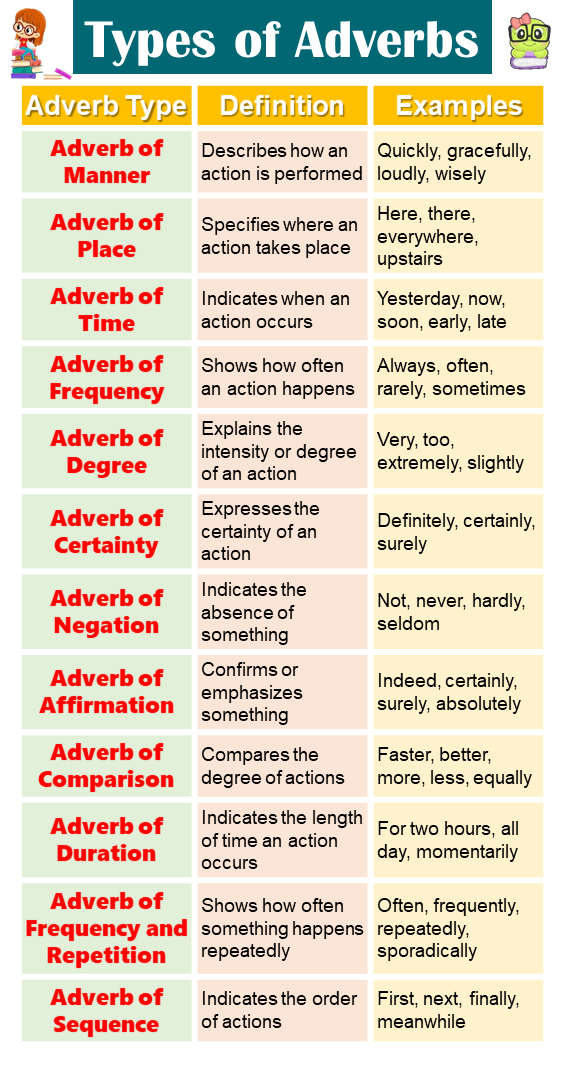
Types of Adverb
Adverbs of Manner
( Here, softly describes how she spoke.)
Adverbs of Time
- We will leave soon.
(In this sentence, Soon indicates when they will leave.)
They can appear at the beginning, middle, or end of a sentence.
Adverbs of Place
- The dog is waiting outside.
Adverbs of Frequency
Adverbs of frequency indicate how often an action occurs. They answer the question "How often?". Words likes: always, often, sometimes, rarely, never, are adverbs of frequency. For exanple:- She always drinks coffee in the morning.
Adverbs of Degree
- He is very tall.
More About Adverb
Adverbial Phrases and Clauses
- She completed the project with great enthusiasm.
Adverbial phrases can provide details about the manner, time, place, or reason of the action.
Adverbial Clauses Definition: An adverbial clause is a dependent clause that acts as an adverb. It contains a subject and a verb and provides information about time, place, condition, reason, or manner. For Example:
- We will leave when the sun sets.
Adverbs for Kids:
An adverb is a word that describes or gives more information about a verb, an adjective, or another adverb. Adverbs tell us how, when, where, or to what extent something happens. For example:
Adverbs are indispensable parts of the language since they are used to extend, give instructions, change nature, and even modify verbs, adjectives and other adverbs. They contain valuable information on how, when, where and to what extent activities take place. It is useful to classify adverbs depending on the manner of expressing them, time, place, frequency, degree, and certainty. First of all, with the help of adverbial phrases and clauses, the details of the grammar can be more diverse.
In sum, the practice of adverbs enhance preciseness and Richness of the message at the interpersonal and transcription level, which can hardly be overemphasised.