What is an Adverb of time?
An adverb of time tells us when something happens or for how long. It gives more information about the time of an action.
- What is an Adverb of time?
- How to use adverb of time in Sentences?
- Adverbs that indicate when:
- Adverbs that indicate for how long:
- Adverbs that indicate for how often:
- Using "yet":
- Using "still":
- Order of Adverbs of Time:
- Adverbs of Time That Indicate Definite Time:
- Adverbs of Time That Indicate Indefinite Time:
- Adverbs of Time That Indicate Duration:
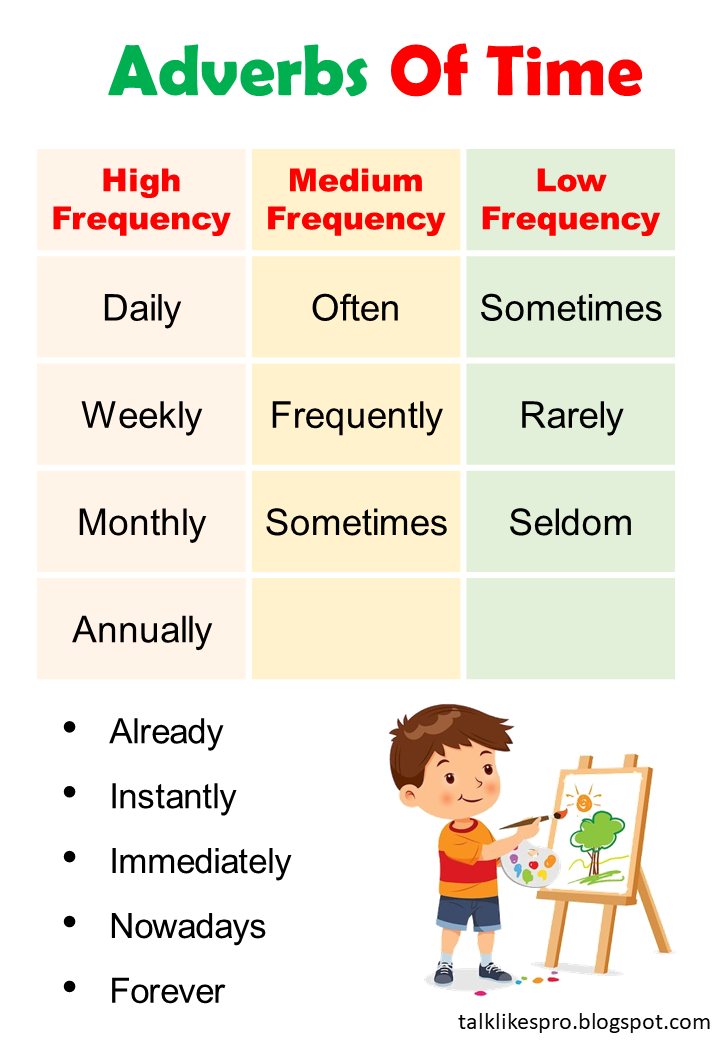
- Adverbs of Time That Indicate Frequency adverbs:
- Combined Example:
- Why is it important to learn about adverbs of time?
Here are some examples:
- Now – She is playing now.
- Yesterday – He visited his grandma yesterday.
- Soon – We will go to the park soon.
- Already – I have already finished my homework.
These words help to specify the timing of the action in a sentence.
How to use adverb of time in Sentences?
Adverbs that indicate when:
Adverbs that tell us when something happens are used to describe the time of an action. Here are some common examples:
- Today – I have a meeting today.
- Tomorrow – She will start her new job tomorrow.
- Yesterday – We went to the beach yesterday.
- Later – I'll call you later.
- Soon – The movie will start soon.
- Now – Let's go now.
These adverbs help answer the question "When?" in a sentence.
An adverb that tells us when normally occupies a position that can be considered central or peripheral; it is an end-position adverb. But all of them may be located in other positions to make the focus changed. Finally, main points adverbs of time can be at the very beginning of the given sentence to emphasize the time period. Some of the following adverbs may be used before the main verb in formal writing, others cannot be used in this position.
Examples:
- Later, the bear ate some porridge. (This highlights the time as significant)
- The bear Later, ate some porridge. (This has a formal tone, similar to a report)
- The bear ate some porridge Later,. (This is neutral, with no special focus on time)
Adverbs that indicate for how long:
Adverbs that indicate for how long provide information about the duration of an action or event. They help answer the question "How long?" Here are some common examples:
- Always – She is always happy.
- Often – They often play soccer after school.
- Sometimes – He sometimes goes to the gym.
- Rarely – I rarely eat dessert.
- Forever – They will be friends forever.
- All day – We worked all day.
In these adverbial phrases which indicate the extent of time for, for is always accompanied by an expression of length of time while since is always accompanied by an expression of a given time.
Example:
- She has lived in this city since 2014.
- He has been working on the project for two months.
- They have been traveling since last summer.
- I’ve known her for a long time.
- We have studied since the morning.
Adverbs that indicate for how often:
Adverbs that tell us how often provide information about the frequency of an action. They help answer the question "How often?" Here are some common examples:
- Always – She always drinks coffee in the morning.
- Usually – They usually go for a walk after dinner.
- Frequently – He frequently travels for work.
- Often – I often read books before bed.
- Sometimes – I sometimes watch movies on weekends.
Stronger: Often, she visits her grandparents.
Weaker: She visits her grandparents often.Stronger: Sometimes, they go hiking on weekends.
Weaker: They go hiking on weekends sometimes.Stronger: Rarely, he eats dessert.
Weaker: He eats dessert rarely.Stronger: Always, I take a walk in the morning.
Weaker: I take a walk in the morning always.
Using "yet":
Using "still":
Order of Adverbs of Time:
When using multiple adverbs of time in a sentence,It can express definite and indefinite time, frequency and duration.
- Definite Time: A certain period as distinguished from another namely: yesterday, today and tomorrow.
- Indefinite Time: General idea of the time – sometime, frequently, scarcely ever, never, always.
- Frequency Adverbs: The frequency of an action – daily basis, weekly basis, monthly basis, yearly basis.
- Duration Adverbs: duration – briefly, momentarily, forever, temporarily.